A binary search tree is a type of ordered binary tree, where the left child has a value smaller than its parent, and the right child has a value greater than or equal to its parent. In a binary search tree, a node has two references, the left child and the right child. A binary search tree with a parent pointer is a variation of a binary search tree – a node has an additional reference to its parent node. Normally a binary search tree’s operations start from the root node. With additional parent pointers, the operations can start from any given node, which improves performance in some cases.
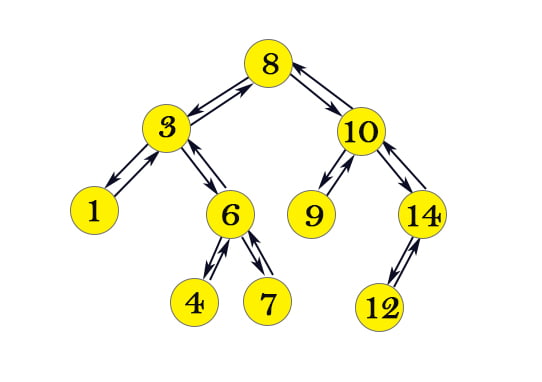
Table of Content
Define classes
A TreeNode class in a binary search tree with a parent pointer has four attributes, data, left, right, and parent. data is the data stored in this node. left is the reference to the left child. right is the reference to the right child. parent is the reference to the parent node.
After you define TreeNode, you can define the BinarySearchTree class. It has one attribute, root.
Please note, in Java, BinarySearchTree’s generic data type extends Comparable interface. So that you can compare data in insertion, deletion, and search operations.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | public class BinarySearchTreeWithParent<T extends Comparable<T>> { //TreeNode with a parent reference static class TreeNode<T> { T data; TreeNode<T> left = null; TreeNode<T> right = null; TreeNode<T> parent = null; //Override, Time O(1), Space O(1) @Override public String toString() { return String.valueOf(data); } } TreeNode<T> root = null; } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | class TreeNode { //Constructor, with parent pointer, Time O(1), Space O(1) TreeNode() { this.left = null; this.right = null; this.parent = null; } //Override, Time O(1), Space O(1) toString() { return this.data; } } class BinarySearchTreeWithParent { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor() { this.root = null; } } |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | class TreeNode : #Constructor, TreeNode with a parent reference, Time O(1) Space O(1) def __init__(self) : self.left = None self.right = None self.parent = None; #Override, Time O(1), Space O(1) def __str__(self): return str(self.data) class BinarySearchTreeWithParent : #Constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) def __init__(self) : self.root = None |
Insert in a binary search tree with parent
To insert a value in a binary search tree, you have to find the right spot, which satisfies the rule of the binary search tree – the parent’s value is larger than the left child’ value, and the right child’s value is larger than the parent’s value.
From root, you compare the input value with each node’s data. If the input value is larger than the node’s data, you move to its right child. Otherwise, move to its left child. You also keep track of the previously visited node and save it in a variable named parent or previous.
When you reach a node whose left or right child is null, you can add the new node with the input value as a left or right child. Meantime, add the reference to the parent in this new node.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | //Insert with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1), h is height of tree public void insert(T value) { TreeNode<T> newNode = new TreeNode<>(); newNode.data = value; if(root == null) { root = newNode; return; } TreeNode<T> curr = root; TreeNode<T> parent; while(true) { parent = curr; if(value.compareTo(curr.data) < 0) { curr = curr.left; if(curr == null) { parent.left = newNode; newNode.parent = parent; return; } } else { curr = curr.right; if(curr == null) { parent.right = newNode; newNode.parent =parent; return; } } } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | //Insert with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1), h is height of tree insert(value) { var newNode = new TreeNode(); newNode.data = value; if(this.root == null) { this.root = newNode; return; } var curr = this.root; var parent; while(true) { parent = curr; if(value < curr.data) { curr = curr.left; if(curr == null) { parent.left = newNode; newNode.parent =parent; return; } } else { curr = curr.right; if(curr == null) { parent.right = newNode; newNode.parent =parent; return; } } } } |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | #Insert with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1), h is height of tree def insert(self, value) : newNode = TreeNode() newNode.data = value if self.root == None : self.root = newNode return curr = self.root parent = None while True : parent = curr if value < curr.data: curr = curr.left if curr == None: parent.left = newNode newNode.parent = parent return else : curr = curr.right if curr == None: parent.right = newNode newNode.parent =parent return |
Delete by key
Deleting a node in a binary search tree with a parent pointer is a little more complicated. First, you find the node with the data that matches the key. Then find its successor. The in-order successor in a binary search tree is the right child’s leftmost descendent. After you replace the deleted node with the successor, you point the successor’s parent to the old parent.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | //Delete with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1) public TreeNode<T> delete(T key) { if (root == null ) return null; if (root.data == key){ //delete root root = deleteNode(root); //reset the root root.parent = null; return root; } TreeNode<T> curr = root; while (true) { if (key.compareTo(curr.data) > 0) { if (curr.right == null ) break; else if (curr.right.data == key) { TreeNode<T> oldParent = curr.right.parent; curr.right = deleteNode(curr.right); if (curr.right != null) curr.right.parent = oldParent; break; } curr = curr.right; } else { if (curr.left == null) break; else if (curr.left.data == key) { TreeNode<T> oldParent = curr.right.parent; curr.left = deleteNode(curr.left); if (curr.left != null) curr.left.parent = oldParent; break; } curr = curr.left; } } return root; } //Delete node, Time O(h), Space O(1) private TreeNode<T> deleteNode(TreeNode<T> node) { if (node == null) return null; if (node.right == null) return node.left; TreeNode<T> curr = node.right; while (curr.left != null) //find the left-most node curr = curr.left; curr.left = node.left; // put the original left under left most, if (node.left!=null) node.left.parent = curr; // link the new far left part to old far left return node.right; } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | //Delete with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1) delete(key) { if (this.root == null ) return null; if (this.root.data == key){ //delete root this.root = this.deleteNode(this.root); //reset the root this.root.parent = null; return this.root; } var curr = this.root; while (true) { if (key > curr.data) { if (curr.right == null ) break; else if (curr.right.data == key) { let oldParent = curr.right.parent; curr.right = this.deleteNode(curr.right); if (curr.right != null) curr.right.parent = oldParent; break; } curr = curr.right; } else { if (curr.left == null) break; else if (curr.left.data == key) { let oldParent = curr.right.parent; curr.left = this.deleteNode(curr.left); if (curr.left != null) curr.left.parent = oldParent; break; } curr = curr.left; } } return this.root; } //Delete node, Time O(h), Space O(1) deleteNode(node) { if (node == null) return null; if (node.right == null) return node.left; var curr = node.right; while (curr.left != null) //find the left-most node curr = curr.left; curr.left = node.left; // put the original left under left most, if (node.left != null) node.left.parent = curr; // link the new far left part to old far left return node.right; } |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | #Delete with parent pointer, Iteration, Time O(h) Space O(1) def delete(self, key) : if self.root == None : return None if self.root.data == key: #delete root self.root = self.deleteNode(self.root) #reset the root self.root.parent = None return self.root curr = self.root while True : if key > curr.data : if curr.right == None : break elif curr.right.data == key: oldParent = curr.right.parent curr.right = self.deleteNode(curr.right) if curr.right != None: curr.right.parent = oldParent break curr = curr.right else : if curr.left == None: break elif curr.left.data == key : oldParent = curr.right.parent curr.left = self.deleteNode(curr.left) if curr.left != None: curr.left.parent = oldParent break curr = curr.left return self.root #Delete node, Time O(h), Space O(1) def deleteNode(self, node) : if node == None: return None if node.right == None: return node.left curr = node.right while curr.left != None: #find the left-most node curr = curr.left curr.left = node.left # put the original left under left most, if node.left != None: node.left.parent = curr # link the new far left part to old far left return node.right |
Free download
Download BinarySearchTreeWithParent.java
Download BinarySearchTreeWithParent.js
Download BinarySearchTreeWithParent.py
Binary tree