Topological sort is a graph traversal in which node v is visited only after all its dependencies are visited. The graph has to be directed and has no cycles, i.e. directed acyclic graph (DAG). Once the graph is built, you can use the algorithms to find the order. The result is not necessary unique. Two algorithms topological sort BFS and DFS are used to solve the problem. They both have linear time O(V+E), V is number of vertices, E is number of edges. Topological sort are usually applied to ranking and scheduling problems. Here is an example to find tournament ranking.
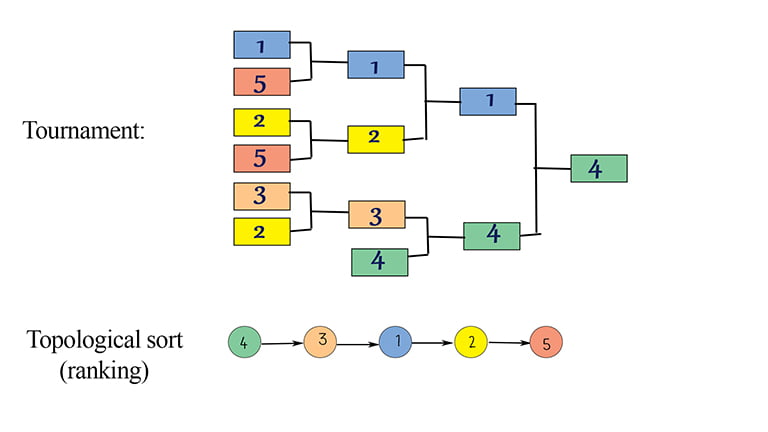
Table of Content
Question statement:
(Modified) In a tennis tournament of N players. The following condition always hold-If player P1 has won the match with P2 and player P2 has won from P3, then Player P1 has also defeated P3. Find winner and ranking of players.
Topological sort dfs uses the data structure stack. For each node and its followers, call the recursion helper. For any node returns from call stack, put it in the stack. The reverse of the stack is the final sorted result.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | import java.util.*; public class FindRankingWithTopoSort<T> { Map<T, LinkedList<T>> adj = new HashMap<>(); //Add edge, Time O(1), Space O(1) public void addEdge(T v, T w) { adj.putIfAbsent(v, new LinkedList<>()); adj.putIfAbsent(w, new LinkedList<>()); adj.get(v).add(w); } //DFS, use stack, Time O(V+E), Space O(V), V is number of nodes, E is number of edges public List<T> topoSortDfs() { Stack<T> stack = new Stack<>(); Map<T, Boolean> visited = new HashMap<>(); for (T key: adj.keySet()) visited.put(key, false); for (T key: adj.keySet()) { if (visited.get(key) == false) dfsHelper(key, visited, stack); } List<T> res = new ArrayList<>(); while (stack.empty() == false) res.add(stack.pop()); return res; } //DFS helper, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) private void dfsHelper(T v, Map<T, Boolean> visited, Stack<T> stack) { visited.put(v, true); for (T i: adj.get(v)) { if (!visited.get(i)) dfsHelper(i, visited, stack); } stack.push(v); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 | class FindWinnerWithTopoSort { constructor() { this.adj = new Map(); } //Add edge, Time O(1), Space O(1) addEdge(v, w) { if (this.adj.get(v) == null) this.adj.set(v, new Array()); if (this.adj.get(w) == null) this.adj.set(w, new Array()); this.adj.get(v).push(w); } // Time O(V+E), Space O(V), V is number of nodes, E is number of edges topoSortDfs() { var stack = []; var visited = new Map(); for (let k of this.adj.keys()) visited.set(k, false); for (let k of this.adj.keys()) { if (visited.get(k) == false) this.dfsHelper(k, visited, stack); } var res = new Array(); while (stack.length > 0) res.push(stack.pop()); return res; } //DFS helper, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) dfsHelper(v, visited, stack) { visited.set(v, true); for (let i of this.adj.get(v)) { if (!visited.get(i)) this.dfsHelper(i, visited, stack); } stack.push(v); } } |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | class FindWinnerWithTopoSort : def __init__(self) : self.adj ={}; #Add edge, Time O(1), Space O(1) def addEdge(self, v, w) : if self.adj.get(v) == None: self.adj[v]= [] if self.adj.get(w) == None: self.adj[w]= [] self.adj[v].append(w) # Time O(V+E), Space O(V), V is number of nodes, E is number of edges def topoSortDfs(self) : stack = []; visited = {}; for k in self.adj.keys(): visited[k] = False; for k in self.adj.keys(): if visited[k] == False: self.dfsHelper(k, visited, stack) res = [] while len(stack) > 0: res.append(stack.pop()) return res # DFS helper, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) def dfsHelper(self, v, visited, stack) : visited[v] = True for i in self.adj.get(v) : if visited[i] == False: self.dfsHelper(i, visited, stack); stack.append(v); |
Doodle
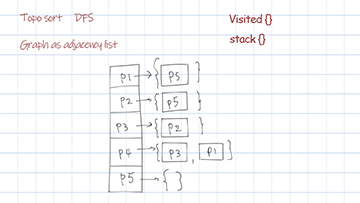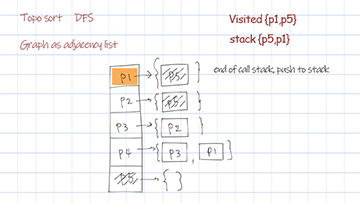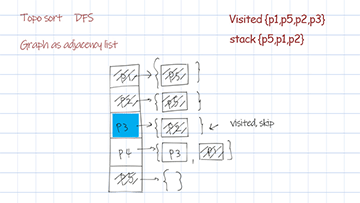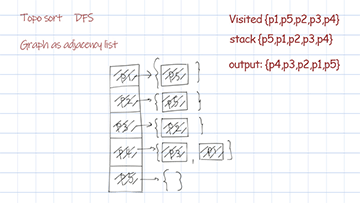
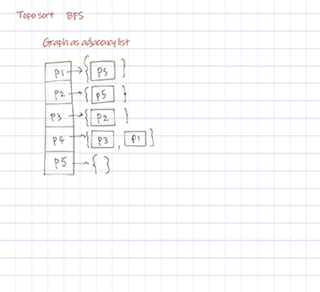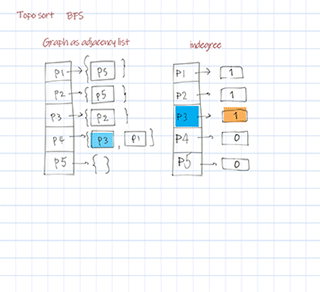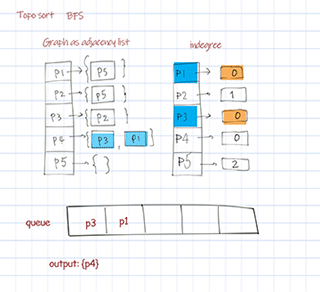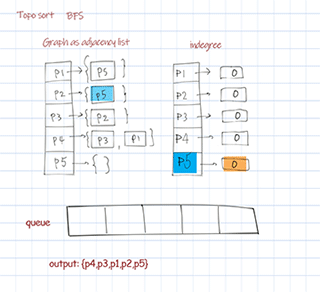
Topological sort BFS uses Kahn’s algorithm. First find a list of start nodes which has no incoming edges, ie indegree is 0. Insert them into a queue. Then pull out items from the queue, update and check its followers’ indegrees. If the indegree is 0, add to the queue. Repeat until all nodes are checked. The sequence pulled from the queue is the final sorted result. The time complexity O(V+E) and space complexity O(V). V is number of nodes (vertices), E is number of edges.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | //BFS Kahn’s algorithm, use indegree, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) public List<T> topoSortBfs() { Map<T, Integer> indegree = new HashMap<>(); for (T key: adj.keySet()) indegree.put(key, 0); for(T key: adj.keySet()) { LinkedList<T> losers = adj.get(key); for(T node : losers) { indegree.put(node, indegree.get(node)+1); } } Queue<T> queue = new LinkedList<T>(); for(T key: adj.keySet()) { if(indegree.get(key) == 0) queue.add(key); } int count = 0; List<T> res = new ArrayList<>(); while(!queue.isEmpty()) { T u = queue.poll(); res.add(u); for(T node : adj.get(u)) { indegree.put(node, indegree.get(node)-1); //decrease indegree by 1 first if (indegree.get(node) == 0) { queue.add(node); } } count++; } if (count != adj.keySet().size()) { //failed to sort return null; } return res; } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | //BFS Kahn’s algorithm, use indegree, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) topoSortBfs() { var indegree = new Map(); for (let key of this.adj.keys()) indegree.set(key, 0); for(let key of this.adj.keys()) { let losers = this.adj.get(key); for(let node of losers) { indegree.set(node, indegree.get(node)+1); } } var queue = new Array(); for(let key of this.adj.keys()) { if(indegree.get(key) == 0) queue.push(key); } var count = 0; var res = new Array(); while(queue.length != 0) { let u = queue.shift(); res.push(u); for(let node of this.adj.get(u)) { indegree.set(node, indegree.get(node)-1); //decrease indegree by 1 first if (indegree.get(node) == 0) { queue.push(node); } } count++; } if (count != this.adj.size) { //failed to sort return null; } return res; } |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | # BFS Kahn’s algorithm, use indegree, Time O(V+E), Space O(V) def topoSortBfs(self) : indegree = {}; for key in self.adj.keys(): indegree[key] = 0 for key in self.adj.keys(): losers = self.adj[key]; for node in losers: indegree[node]= indegree[node]+1 queue = [] for key in self.adj.keys() : if indegree.get(key) == 0 : queue.append(key); count = 0 res = [] while len(queue) != 0: u = queue.pop() res.append(u) for node in self.adj[u]: indegree[node] = indegree[node]-1 #decrease indegree by 1 first if indegree[node] == 0: queue.append(node) count += 1; if count != len(self.adj): #failed to sort return None return res |
Doodle
Output:
{P1=[P5], P2=[P5], P3=[P2], P4=[P3, P1], P5=[]}
Topological sort dfs: [P4, P3, P2, P1, P5]
Topological sort bfs: [P4, P3, P1, P2, P5]
O Notation:
Time complexity: O(V+E)
Space complexity: O(V)
V is number of nodes, E is number of edges
Download
Download FindRankingWithTopoSort.java
Download FindRankingWithTopoSort.js
Download FindRankingWithTopoSort.py