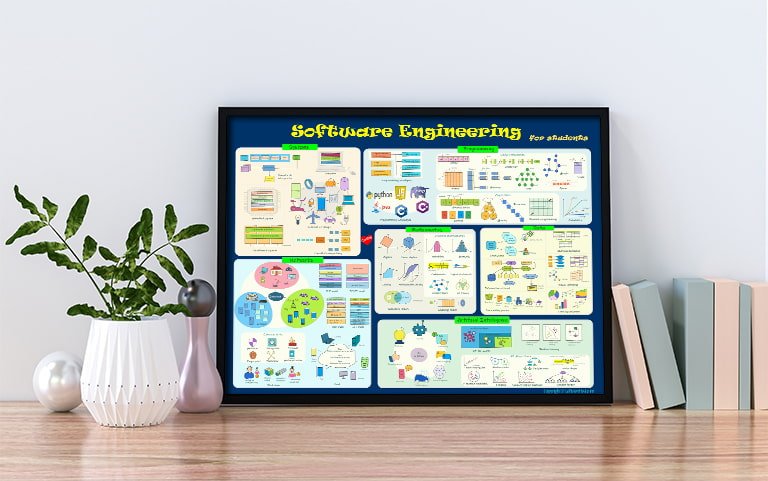
This post is an illustrated explanation of Software Engineering Concepts and terminologies. It helps you to decide which areas you would like to specialize in.
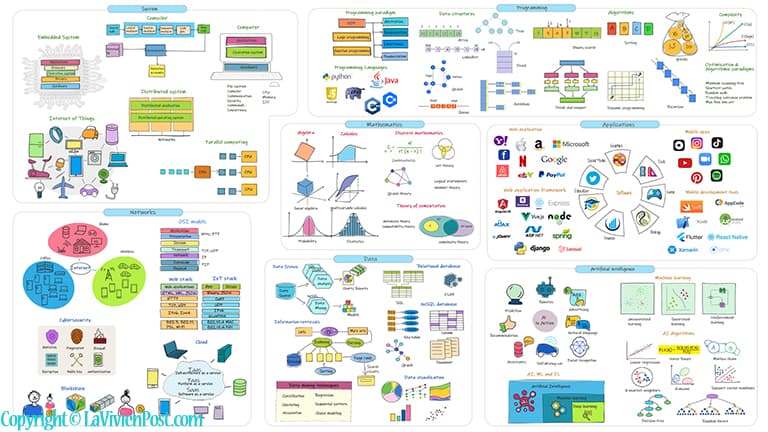
Table of Content
- Mathematics
- Systems
- Programming
- Networks
- Data Science
- Applications
- Artificial intelligence
- For your consideration
1. Mathematics
Mathematics is an important foundation for all science and engineering disciplines. You probably have learned algebra and calculus in middle school or high school. Certain subjects of mathematics like linear algebra, multivariable calculus, probability, and statistics, are purely related to computer programming.
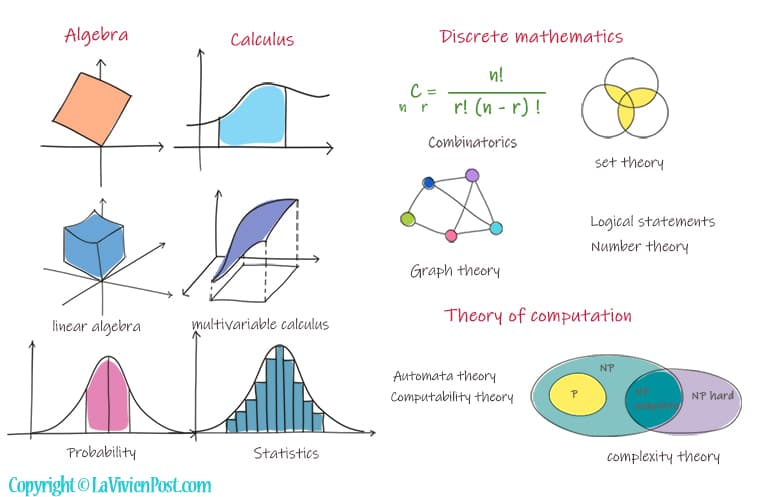
Algebra focuses on equations with variables. Linear algebra concerns linear equations, linear maps, and their representations in vector spaces and through matrices.
Calculus needs more brainwork than algebra to understand. Calculus is the study of continuous change between values that are related by a function. Multivariable calculus studies functions of multiple real variables.
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that are countable, distinct, or separable. They are foundations for software engineering and information systems.
One of them is probability. A probability is a number, between 0 and 1 inclusive, that represents the likelihood of an event. Statistics is the application of probability theory – the collection, and analysis of data.
Other topics in discrete mathematics include combinatorics, set theory, graph theory, logical statements, and number theory.
If you are a computer science major, you will probably study the Theory of computation. The theory of computation deals with how to efficiently solve problems on a model of computation using an algorithm. It has sub-sections as Automata theory, computability theory, and complexity theory.
2. Systems
Computer systems are a must-know for all students in computer majors. A computer is built of various components hardware and software. The hardware includes the CPU, memory, buses, Io devices, etc.
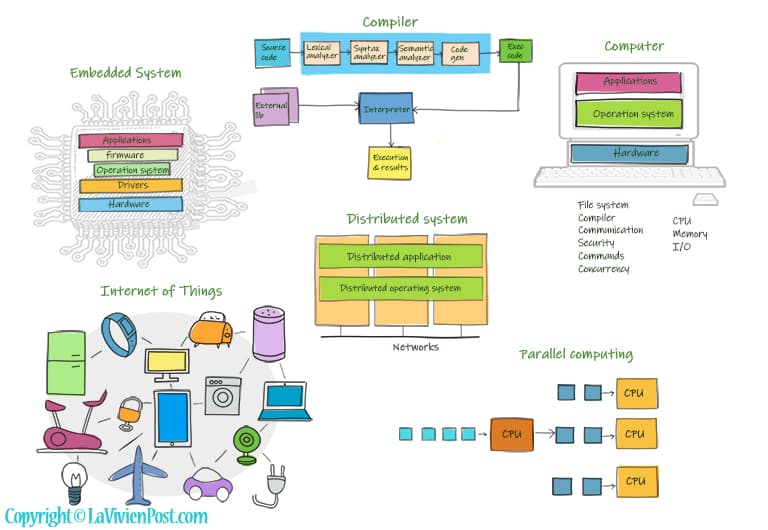
The software includes operation systems and applications. The operating system manages the computer’s memory and processors, as well as all the software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer. Common desktop operating systems include Windows, MacOS, and Linux.
Compilers are programs that help to convert source Code into machine executable codes. A compiler performs the following operations: lexical analysis, syntax analysis, semantic analysis, and code generation. Interpreters execute the code and output the result.
An embedded system is a mini computer in a chip or a device. Like a computer, it has hardware, an operation system, and applications. It might also have a device driver and firmware in order to function. The mobile phones and medical devices are embedded systems.
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of wireless devices around the world that are connected to the Internet. They all collect and share data.
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers. They communicate with one another and coordinate to appear as a single coherent system. Distributed Operating Systems can manage multiple CPUs used by Distributed systems to serve multiple real-time applications and multiple users.
Parallel computing refers to the calculations or the execution of processes that are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time.
3. Programming
Programming is the most essential part of software engineering. Programming languages are probably the most debated topic for developers. The current top-used languages are Python, JavaScript, PHP, Java, C# and C++. Python is popular in Artificial intelligence. PHP and JavaScript are used in web applications. Java and C# are options to build big enterprise applications. C++ is good for embedded systems.
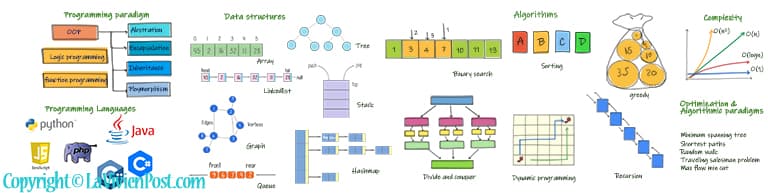
Programming paradigm refers to the way you program. It does not refer to a specific language. For example, there are object-oriented programming, logic programming, and functional programming.
Object-oriented programming, OOP has been dominant in recent years. OOP is Programming by defining objects that interact with each other. There are 4 principles: Abstraction, Encapsulation, Inheritance, Polymorphism. Doing it right, developers write less code and make a highly scalable application.
Data structures refer to the way how data are organized and manipulated. The most used data structures are arrays, linked lists, maps, trees, stacks, queues, and graphs. Developers consistently seek ways to make data access more efficient.
An algorithm is a set of instructions or recipes that describes the exact steps to solve a problem. The commonly used algorithms are binary searching, sorting algorithms, divide and conquer, greedy algorithms, backtracking and recursion, and dynamic programming.
Complexity is the measure of the efficiency of the algorithms or solutions. They are evaluated by time and space at worst scenarios. It gives a good indication of performance for large amounts of data.
Optimization is the constant effort carried out by computer scientists and engineers. Here are a few well-known topics or algorithmic paradigms: minimum spanning tree, shortest paths, random walk, traveling salesman problem, max flow min cut, np-complete problems, etc.
4. Networks
Computer Networks is to use communication protocols to share information by computers located on the network nodes. In the office buildings, the computers are connected by local networks. When you work remotely from home, you connect to the internet by routers. On the road, you connect your wireless devices through 4G/5G.
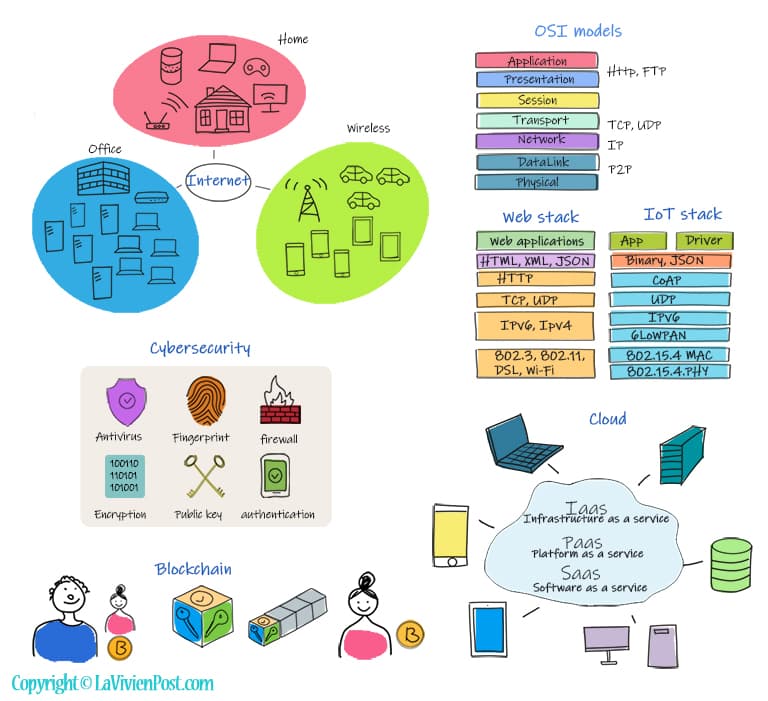
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) is the primary architectural model for Internet communications. The OSI model splits the communication process into 7 layers. From the bottom up, they are physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application.
Network protocols are standard rules for formatting data in digital communication. At each layer of the OSI model, there are protocols you may already have heard of: HTTP used in web applications; FTP for file transfer, TCP and IP used in routers, peer to peer (p2p) in the decentralized system. Two examples of TCP/IP models are the web stack and IoT stack.
Cybersecurity has become a very important subject in computer networks. Cybersecurity is the collection of technologies and processes to protect computers and systems from cyberattacks. The technologies include firewalls, authentication, antivirus, fingerprint, cryptography, digital certification, etc.
Blockchain is digitized transactions through a secured, shared, and distributed ledger on the internet. Bitcoin is powered by blockchain technology. When two parties conduct a transaction, the process includes assigning cryptographic keys, validating the transaction, creating a block, appending the new block in the blockchain, and completing the transaction.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet. There are three main service models – Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). The most popular cloud service providers are Amazon web services AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
5. Data Science
One major task of the Computer is processing data. This includes data collection, process, management, storage, and analysis. Data science came to the spotlight due to big data. Data science uses scientific methods, and algorithms to extract knowledge and insights from structural and unstructured data. Meanwhile, data mining emerges.
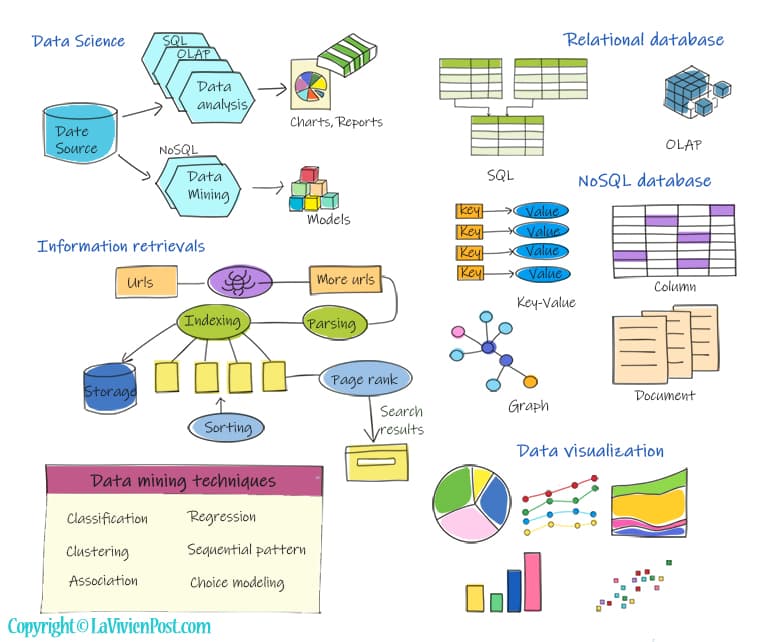
Information retrievals have been with us for decades. From a URL, a crawler is used to collect data and more links. Next is to parse and index data, then store them. sorting, page Ranking, and other algorithms are applied to the process. At the end, users can retrieve the most relevant data.
A database is an organized collection of structured information. There are two types of database- relational database and NoSQL database. A relational database organizes data into tables. The schema and SQL are used. Schema represents the design of how the data is organized in terms of tables and attributes. SQL is the language to query data. The most popular relational databases are Oracle, SQL server, and MySQL.
NoSQL database refers to any non-relational database. it doesn’t use tables or strict schema. Instead, 4 types of data structures are used, document, key-value, wide-column, and graph. They can scale easily with large amounts of data and high user loads. The popular NoSQL databases are Mongo dB, Amazon DynamoDB, Cassandra, etc.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information. It uses visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps. It provides an intuitive way to see and understand the data.
Data mining uses a broad range of techniques, to look out for patterns and trends that can’t be found using simple analysis techniques. The techniques include classification, clustering, regression, sequential pattern, and association. Apache Hadoop and spark are one of the tools that are widely used to do the job.
6. Applications
Application software is a program or group of programs designed for end-users. The software has been applied in almost every sector of our society, such as finance, biology, commerce, education, tools, games, and computer graphics. Here we only focus on 2 areas that attract a lot of talented software engineers – Web applications and mobile applications.
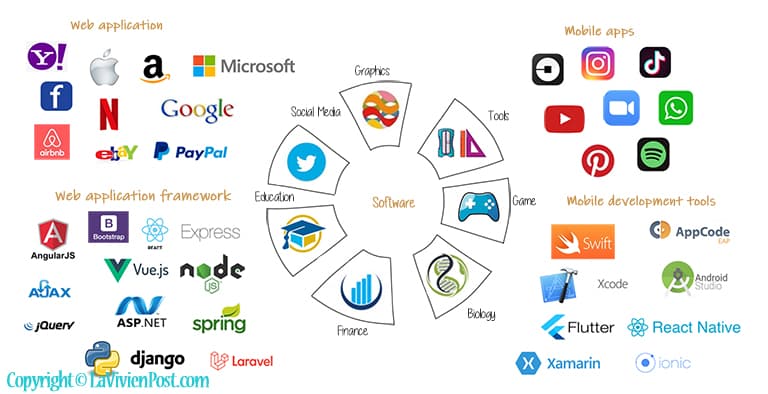
A web application is application software that runs on a web server and is accessed by the user through a web browser. These applications are usually programmed using a client–server structure. The most successful tech companies provide software on the web, such as Google search, amazon e-commerce, Netflix video streaming, and Facebook social media.
Writing web applications is often simplified by the use of a web application framework, A web framework is a software framework that is designed to support the development of web applications including web services, web resources, and web APIs. The examples are ASP.net for C#, Spring for Java, Django for Python, and Angular for JavaScript. When you dedicate to web applications, you should be familiar with databases, web servers, the MVC pattern, and web programming languages such as JavaScript, Ajax, JSON, etc.
Mobile applications have become an inseparable part of our lives. From socializing, shopping, travel booking, and learning, to watching our favorite movies and TV shows, we have a mobile app for almost everything.
Some of the latest mobile development tools include Android Studio, AppCode, and Xcode; languages include Java, Swift, and Objective-C. While doing web applications and Mobile applications, the factors to consider are timeline, scalability, security, and complexity.
7. Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence means machine or computer behaves like a intelligent beings. It gets significate attraction recently because of its practical uses in real world, such as image recognition, natural language processing, speech recognition, facial recognition, robotics, recommendation system etc.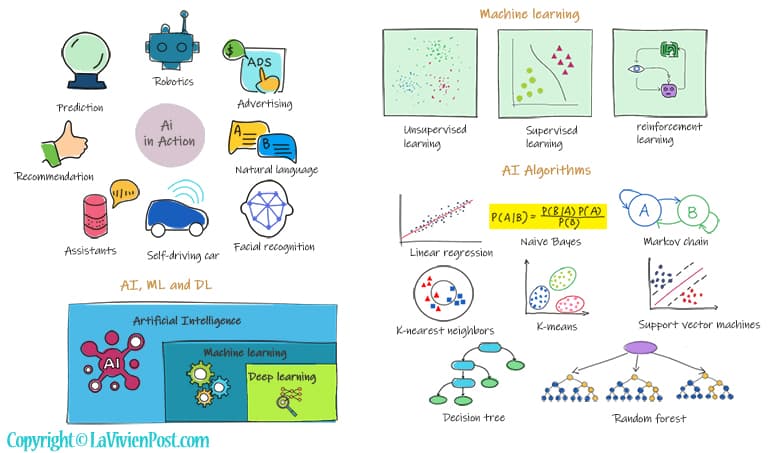
Any intelligence is a combination of Reasoning, learning, problem-solving perception, language understanding, etc. The reasoning is the process of deriving logical conclusions and making decisions from existing data. Probabilistic reasoning is to apply the concept of probability to indicate the uncertainty in knowledge.
As far as learning, there are different kinds of learning in artificial intelligence. Machine learning is a subset of AI that allows machines to learn from data without being assisted by humans. Deep learning enables this automatic learning through the absorption of huge amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, or video. Neural networks mimic the human brain through a set of algorithms. It makes up the backbone of deep learning algorithms.
Machine learning can be divided into three types: unsupervised learning, supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. In Supervised learning, All data is labeled and the algorithms learn to predict the output from the input data. In unsupervised learning, All data is unlabeled and the algorithms learn to inhere structure from the input data. Reinforcement learning is the strategy in which an agent takes actions in the environment to maximize the reward.
AI relies on mathematics and algorithms heavily. You should be comfortable with multivariable calculus, linear algebra, probability theory, and complexity theory before studying AI. While studying AI, you will learn the following algorithms in depth, Naive Bayes, Markov decision process, K-nearest neighbors, K means, decision tree, and random forest.