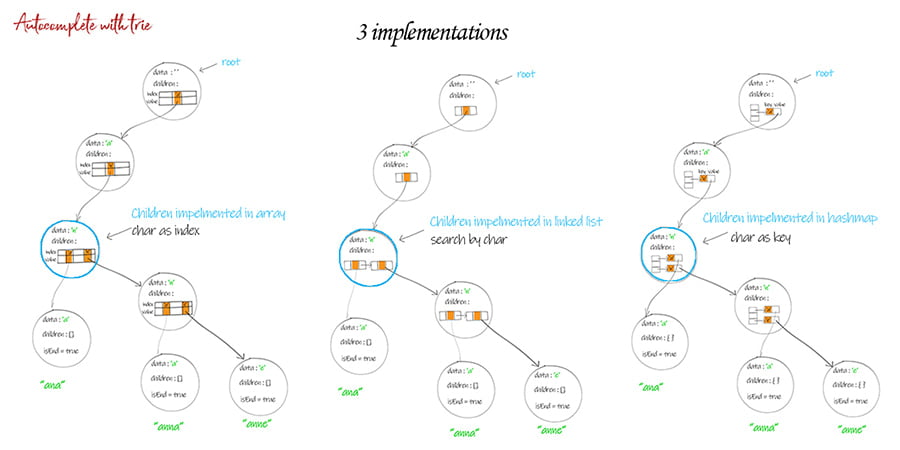
Autocomplete is a feature that search box returns the suggestions based on what you have typed. Autocomplete with trie provides an implementation of auto-complete by using data structure trie.
A trie is a tree-like data structure in which every node stores a character. After building the trie, strings or substrings can be retrieved by traversing down a path of the trie. First we define the TrieNode, which includes data, children and isEnd. The data is the character the node stores. The isEnd is to mark whether this node is the last node of a word. The children is the links to the nodes which hold next letter in the word. The children can be implemented with array, linked list, and hash map. Each implementation has its pros and cons. Take a loot at graph below to see the differences. Next we define Trie class, in which there are methods such as insert, search etc.
To implement autocomplete, we start from the root of the trie, navigate to the node which holds the last letter of the prefix (the input string). From there, we call the recursive method to find all the nodes branched from the last node of prefix. This method is the same as pre-order of the tree from the root. The time complexity is O(n). n is the number of nodes included (Prefix and branches).
There are three solutions, using array, linked list and hash map. All implementations have been provided in Java, JavaScript and Python.
Table of Content
- Implementation 1: Children is defined as array (popular)
- Implementation 2: Children is defined as linked list
- Implementation 3: Children is defined as hash map(Best solution)
- Download
Amazon Interview Question:
Implement autocomplete using trie. When searching “amaz”, it should return words that start with “amaz” such as “amazon”, “amazon prime”, “amazing” etc.
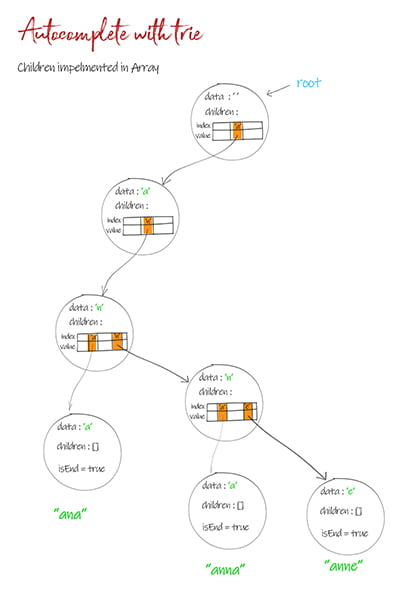
Implementation 1: Children is defined as array
This is the most intuitive implementation. If all words are alphabets a-z, the array size is 26. If there are special characters such as space, the array size is 128. Since it is constant, it wouldn’t affect the complexity. But it takes more memory spaces.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 | import java.util.*; public class AutocompleteTrieArray { //don't use 26 if there is space or any other special characters static final int NUM_OF_CHARS = 128 ; static class TrieNode { char data; TrieNode[] children = new TrieNode[NUM_OF_CHARS]; boolean isEnd = false; //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1), 128 is constant TrieNode(char c) { data = c; } } static class Trie { TrieNode root = new TrieNode(' ') ; //Inserts a word into the trie, Iteration //Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length void insert(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char ch: word.toCharArray()) { if (node.children[ch] == null) node.children[ch] = new TrieNode(ch); node = node.children[ch]; } node.isEnd = true; } //find the node with prefix's last char, then call helper to find all words using recursion //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes included(prefix and branches) List<String> autocomplete(String prefix) { TrieNode node = root; List<String> res = new ArrayList<String>(); for (char ch: prefix.toCharArray()) { node = node.children[ch]; if (node == null) return new ArrayList<String>(); } helper(node, res, prefix.substring(0, prefix.length()-1)); return res; } //recursion function called by autocomplete //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches void helper(TrieNode node, List<String> res, String prefix) { if (node == null ) //base condition return; if (node.isEnd) res.add(prefix + node.data); for (TrieNode child: node.children) helper(child, res, prefix + node.data); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Trie t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("apple"); System.out.println(t.autocomplete("amaz")); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | class TrieNode { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor(c) { this.data = c; this.children = {}; //array this.isEnd = false; } } class Trie { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor() { this.root = new TrieNode(''); } //insert a word into the trie, iteration //Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length insert(word) { let node = this.root; for (let ch of word) { if (node.children[ch]== null) node.children[ch] = new TrieNode(ch); node = node.children[ch]; } node.isEnd = true; } //returns all words with given prefix, call recursion function //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes included(prefix and branches) autocomplete(prefix) { var node = this.root; var res = []; for (let ch of prefix) { node = node.children[ch]; if (node == null) return res; } this.helper(node, res, prefix.substring(0, prefix.length-1)); return res; } //recursive function called by autocomplete //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches helper(node, res, prefix) { if (node.isEnd) res.push(prefix + node.data); for (let child in node.children) //array this.helper(node.children[child], res, prefix + node.data); } } const t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("ebay"); a = t.autocomplete("amaz"); console.log(a); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | class TrieNode: #Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1), 128 is constant def __init__(self, c): self.children = [None]*128 #don't use 26 if there is space or other special characters self.isEnd = False self.data = c class Trie: #Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) def __init__(self): self.root = TrieNode('') #inserts a word into the trie, Iteration, #Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length def insert(self, word): node = self.root for ch in word: idx = ord(ch) if not node.children[idx]: node.children[idx] = TrieNode(ch) node = node.children[idx] node.isEnd = True #returns all words with given prefix #Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes included(prefix and branches) def autocomplete(self, prefix): node = self.root res = [] for ch in prefix: node = node.children[ord(ch)] if node == None: return [] self.helper(node, res, prefix[:-1]) return res #recursion function called by autocomplete, Time O(n), Space O(n) # n is number of nodes in bra def helper(self, node, res, prefix): if node == None: return if node.isEnd : res.append(prefix + node.data) for child in node.children: self.helper(child, res,prefix + node.data) t = Trie() t.insert("amazon") t.insert("amazon prime") t.insert("amazing") t.insert("amazing spider man") t.insert("amazed") t.insert("apple") print(t.autocomplete('amaz')) |
Doodle
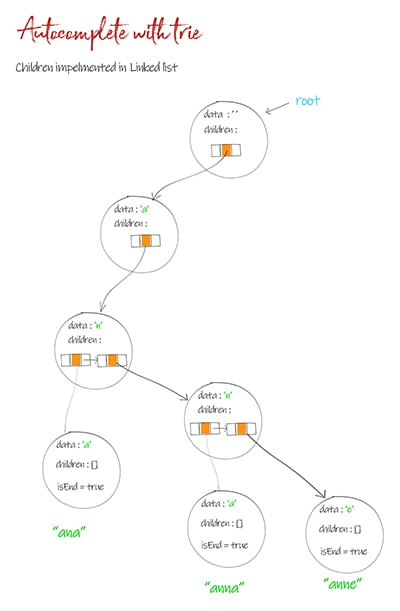
Implementation 2: Children is defined as linked list
The linked list implementations overcome the space problem in Array. The node is created only needed. but it takes time to search the node by char. The same as array size, the longest list size is limited to 26 or 128, based on what characters in the words.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 | import java.util.*; public class AutocompleteTrieList { static class TrieNode { char data; LinkedList<TrieNode> children = new LinkedList<>(); boolean isEnd = false; //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) TrieNode(char c) { data = c; } //find the node by char, the same functionality as children[ch] in array implementation //Time O(k), Space O(1), k is number of children of this node TrieNode getChild(char c) { if (children != null) for (TrieNode child : children) if (child.data == c) return child; return null; } } static class Trie { TrieNode root = new TrieNode(' '); //Add a word to trie, Iteration, Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length void insert(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) { if (node.getChild(ch) == null) node.children.add(new TrieNode(ch)); node = node.getChild(ch); } node.isEnd = true; } //find the node with prefix's last char, then call helper to find all words using recursion //Recursion, Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) List<String> autocomplete(String prefix) { TrieNode node = root; List<String> res = new ArrayList<String>(); for (char ch: prefix.toCharArray()) { //find end of prefix node = node.getChild(ch); if (node == null) return new ArrayList<String>(); } helper(node, res, prefix.substring(0, prefix.length()-1)); return res; } //recursion helper, Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches void helper(TrieNode node, List<String> res, String prefix) { if (node.isEnd) res.add(prefix + node.data); for (TrieNode child : node.children) helper(child, res, prefix + node.data); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Trie t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("apple"); System.out.println(t.autocomplete("amaz")); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | class TrieNode { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor(c) { this.data = c; this.children = new Array(); //List this.isEnd = false; } //find the node by char, the same functionality as children[ch] in array implementation //Time O(k), Space O(1), k is number of children of this node getChild(c) { if (this.children != null) for (let child of this.children) if (child.data == c) return child; return null; } } class Trie { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor() { this.root = new TrieNode(''); } //insert a word into the trie, Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length insert (word) { var node = this.root; for (let ch of word) { if (node.getChild(ch) == null) node.children.push(new TrieNode(ch)); node = node.getChild(ch); } node.isEnd = true; } //find all word with given prefix, call recursion function //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) autocomplete (prefix) { var node = this.root; var res = new Array(); for (let ch of prefix) { //find end of prefix node = node.getChild(ch); if (node == null) return new Array(); } this.helper(node, res, prefix.substring(0, prefix.length-1)); return res; } //recursive function called by autocomplete //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches helper (node, res, prefix) { if (node.isEnd) res.push(prefix + node.data); for (let child of node.children) //list this.helper(child, res, prefix + node.data); } } const t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("apple"); a = t.autocomplete("amaz"); console.log(a); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 | class TrieNode: #Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) def __init__(self, c): self.data = c self.children = [] # list self.isEnd = False #find the node by char, the same functionality as children[ch] in array implementation #Time O(k), Space O(1), k is number of children of this node def getChild(self, c): if self.children != None: for child in self.children: if child.data == c: return child return None class Trie: #Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) def __init__(self): self.root = TrieNode('') #Add a word to trie, Iteration, Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length def insert(self, word) : node = self.root for ch in word: if node.getChild(ch) == None: node.children.append(TrieNode(ch)) node = node.getChild(ch) node.isEnd = True #find all word with given prefix #Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) def autocomplete(self, prefix): node = self.root res = [] for char in prefix : node = node.getChild(char) if node == None: return [] self.helper(node, res, prefix[:-1]) return res #recursive function called by autocomplete #Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches def helper(self, node, res, prefix) : if node.isEnd: res.append(prefix + node.data); for child in node.children: self.helper(child, res, prefix + node.data) t = Trie() t.insert("amazon") t.insert("amazon prime") t.insert("amazing") t.insert("amazing spider man") t.insert("amazed") t.insert("apple") print(t.autocomplete('amaz')) |
Doodle
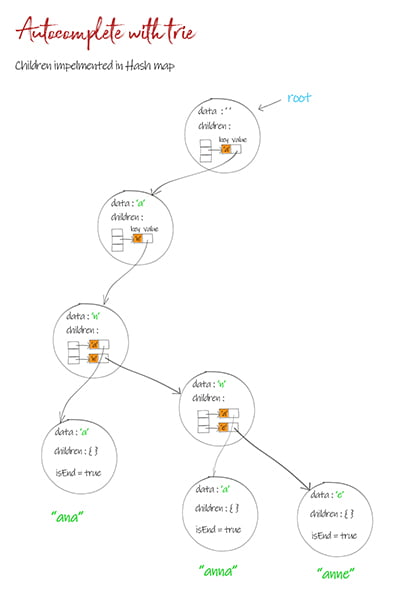
Implementation 3: Children is defined as hash map
This is similar to array implementation. In stead of using char as index, it uses char as the key in the hash map. It is the best solution since it doesn’t need to declare 26~128 long array in each trie node.
Java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 | import java.util.*; public class AutocompleteTrieMap { static class TrieNode { char data; HashMap<Character, TrieNode> children = new HashMap<>(); boolean isEnd = false; //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) TrieNode(char c) { this.data = c; } } static class Trie { TrieNode root = new TrieNode(' '); //Add a word to trie, Iteration, Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length void insert(String word) { TrieNode node = root; for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) { if (!node.children.containsKey(ch)) node.children.put(ch, new TrieNode(ch)); node = node.children.get(ch); } node.isEnd = true; } //find all word with given prefix //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) List<String> autocomplete(String prefix) { List<String> res = new LinkedList<String>(); TrieNode node = root; for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) { if (node.children.containsKey(ch)) node = node.children.get(ch); else return res; } helper(node, res, prefix.substring(0, prefix.length()-1)); return res; } // recursive function called by autocomplete //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches void helper(TrieNode node, List<String> res, String prefix) { if (node.isEnd) res.add(prefix + node.data); for (Character ch : node.children.keySet()) helper(node.children.get(ch), res, prefix + node.data); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Trie t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("apple"); System.out.println(t.autocomplete("amaz")); } } |
JavaScript
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 | class TrieNode { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor(c) { this.data = c; this.isEnd = false; this.children = new Map(); //map } } class Trie { //Constructor, Time O(1), Space O(1) constructor() { this.root = new TrieNode(''); } //inserts a word into the trie. Time O(s), Space O(s), s is word length insert (word) { var node = this.root; for (let ch of word) { if (!node.children.has(ch)) node.children.set(ch, new TrieNode(ch)); node = node.children.get(ch); } node.isEnd = true; } //find all word with given prefix, call recursion function //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) autocomplete (word) { var res = new Array(); var node = this.root; for (let ch of word) { if (node.children.has(ch)) node = node.children.get(ch); else return res; } this.helper(node, res, word.substring(0, word.length-1)); return res; } //recursive function called by autocomplete //Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches helper (node, res, prefix) { if (node.isEnd) res.push(prefix + node.data); for (let c of node.children.keys()) this.helper(node.children.get(c), res, prefix + node.data); } } const t = new Trie(); t.insert("amazon"); t.insert("amazon prime"); t.insert("amazing"); t.insert("amazing spider man"); t.insert("amazed"); t.insert("ebay"); t.insert("apple"); a = t.autocomplete("amaz"); console.log(a); |
Python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | class TrieNode: #constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) def __init__(self, c): self.data = c self.isEnd = False self.children = {} #map class Trie: #constructor, Time O(1) Space O(1) def __init__(self): self.root = TrieNode('') #Add a word to trie, Time O(s) Space O(1) s is word length def insert(self, word): node = self.root for ch in word: if not ch in node.children: node.children[ch] = TrieNode(ch) node = node.children[ch] node.isEnd = True #find all word with given prefix #Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes involved (include prefix and branches) def autocomplete(self, word): res = [] node = self.root for ch in word: if ch in node.children: node = node.children[ch] else: return [] self.helper(node, res, word[:-1]) #except the last "ama", node is "z" return res #recursive function called by autocomplete #Time O(n), Space O(n), n is number of nodes in branches def helper(self, node, res, prefix): if node.isEnd: res.append(prefix + node.data) for child in node.children.values(): self.helper(child, res, prefix + node.data) t = Trie() t.insert("amazon") t.insert("amazon prime") t.insert("amazing") t.insert("amazing spider man") t.insert("amazed") t.insert("apple") a = t.autocomplete("amaz") print(a) |
Doodle
Output:
amazon
amazon prime
amazing
amazing spider man
amazed
O Notation:
Time complexity: O(n), n is number of nodes included (Prefix and branches)
Space complexity: O(n)
To implement autocomplete, we start from the root of the trie, navigate to the node which holds the last letter of the prefix (the input string). From there, we call the recursive method to find all the nodes branched from the last node of prefix. This method is the same as pre-order of the tree from the root. The time complexity is O(n). n is the number of nodes included (Prefix and branches).
Download
Download AutocompleteWithTrieJava.zip
Download AutocompleteWithTrieJavaScript.zip
Download AutocompleteWithTriePython.zip
Autocomplete with trie (YouTube)
Java Coding Interview Pocket Book (2nd Edition)