PyTorch is an open-source machine learning framework originally from Meta Ai. If you want to study AI or work on AI projects, setting up a development environment with PyTorch on a local machine is essential for many projects. GPU (Graphics processing unit) is a specialized processor originally designed to process data simultaneously. It helps to speed up the computation of your deep-learning code. This is a complete guide to install PyTorch GPU on Windows. The installation involves many steps. Let’s get started.
Table of Content
- Download Nvidia graphics driver
- Install Visual Studio Community
- Check software compatibilities at PyTorch site
- Install CUDA Toolkit 12.4
- Install cuDNN 8.9.7
- Install Anaconda3
- Create virtual environment for TyPorch
- Install PyTorch
- Run your project
- Install PyCharm
1. Download Nvidia graphics driver
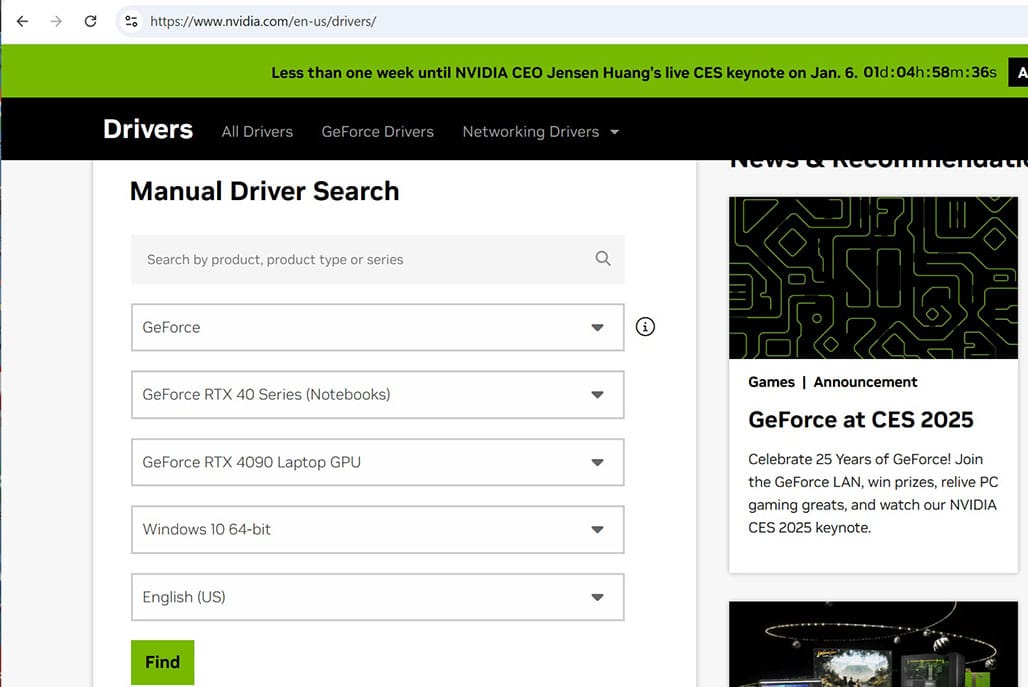
If you already have a PC with GPU, you can skip this step. If you are going to get a new machine learning PC with GPU, please check CUDA enabled GPU cards before buying one. I suggest you buy a PC with a Nvidia graphic card having at least 12GB GDDR6 or GDDR6X. If you just got a new PC with Nvidia GPU, you go to Nvidia driver to download the graphic card driver. After downloading, you run the exe file to install.
2. Install Visual Studio Community
Note: if you already have installed the Nvidia CUDA toolkit and library, you can skip the next three steps.
To compile and support the Nvidia toolkit and library, you need a C++ compiler. You go to Visual Studio 2022. Go to Visual studio download page. Select community and click Free download. Run the installer. Select three elements to install: Python development, desktop c++, and visual studio extension development.
Run the installer to finish the installation.
3. Check software compatibilities at PyTorch site
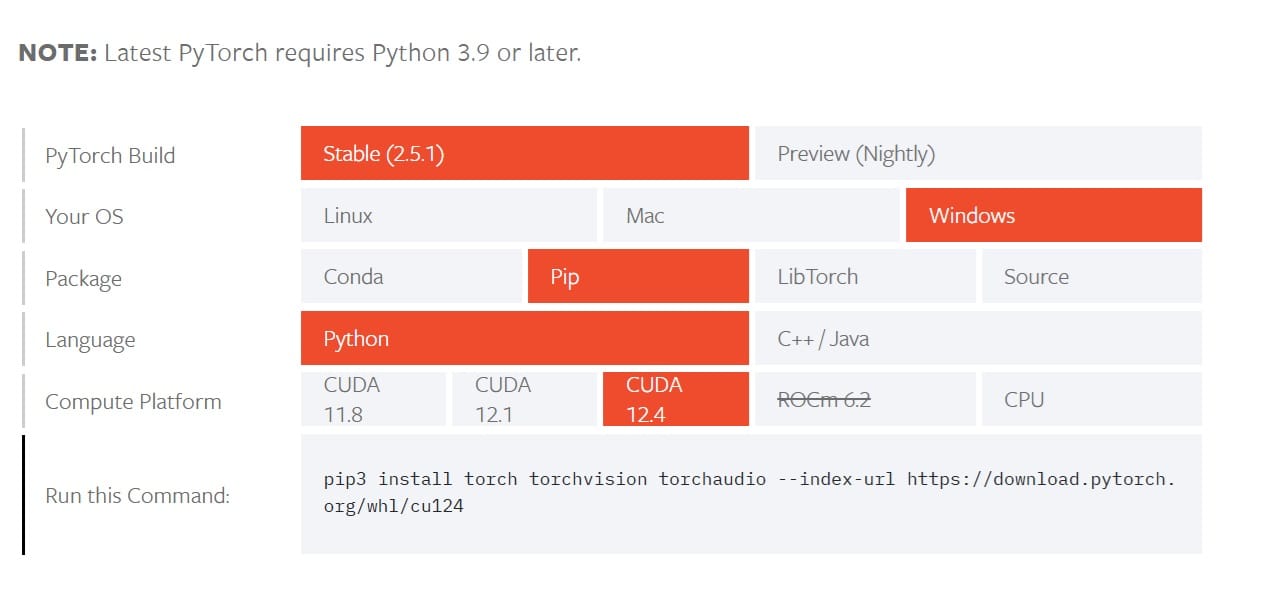
Go to PyTorch Set Started Page to get software requirements and compatibilities. You have options to choose CUDA 11.8, CUDA 12.1 or CUDA 12.4. Let’s pick the latest one 12.4
4. Install CUDA Toolkit 12.4
CUDA is a software layer that gives direct access to the Nvidia GPU’s virtual instruction set and parallel computational elements. Go to CUDA Toolkit archive at Nvidia, Click the link of CUDA ToolKit 12.4.0. In the next window, select Windows, the version of your operation system, and the installer type, you can download and follow the default to install it.
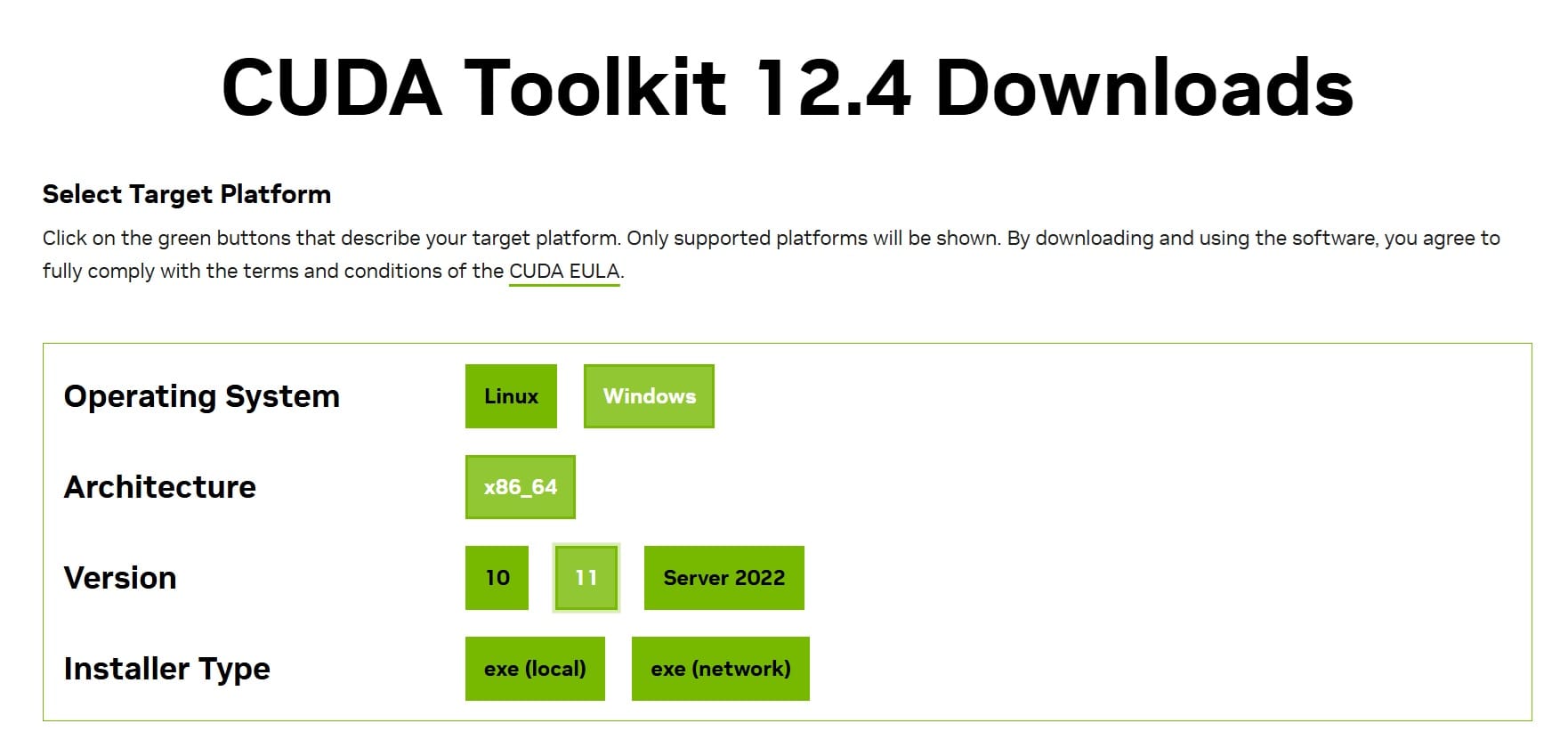
It is installed at C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.4.
5. Install cuDNN 8.9.7
The Nvidia CUDA® Deep Neural Network Library (cuDNN) is a GPU-accelerated library of primitives for deep neural networks. Go to Nvidia’s cuDNN Archive, and download cuDNN v8.9.7 for CUDA 12.x.
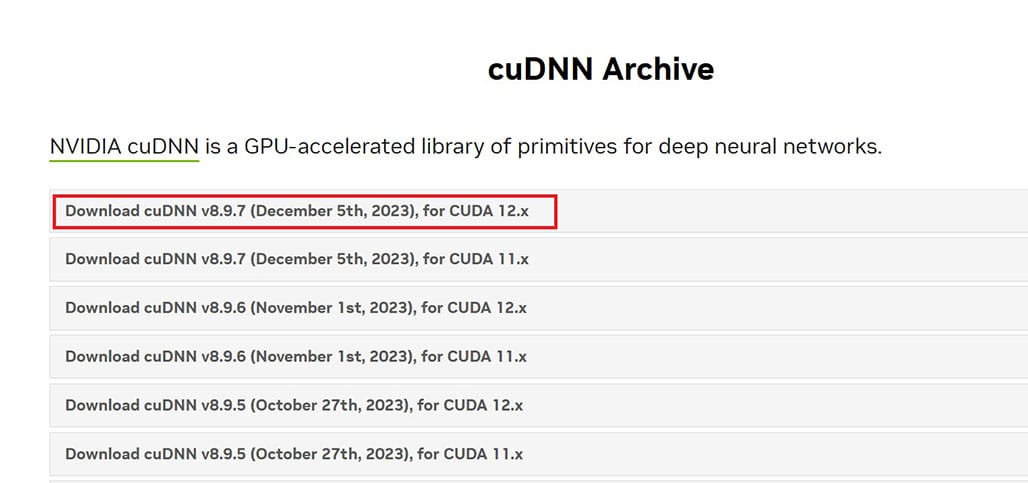
Extract the downloaded zip file and copy three subfolders, i.e. include, lib and bin.
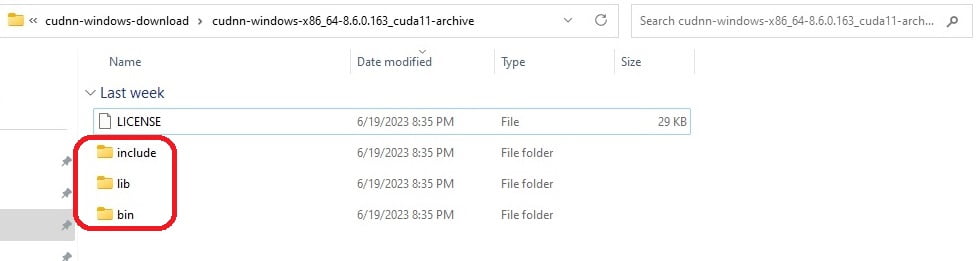
Paste them to the CUDA install directory C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.4\. New files are added to CUDA.
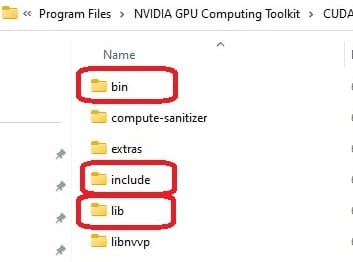
Open the “Environment Variables” window, and add the following new two paths:
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.4\bin
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v12.4\libnvvp
6. Install Anaconda3
Conda is an open-source package and environment management system that runs on Windows, macOS, and Linux. Conda quickly installs, runs, and updates packages and their dependencies. To install, go to Anaconda site to download Anaconda installer, click the download button, or click the link for windows.
After you run the installer, Anaconda3 is installed at C:\Users\yourusername\anaconda3. It also installs Python 3.12 there. Remember to add the following paths in “Environment Variables”:
C:\Users\yourusername\anaconda3
C:\Users\yourusername\anaconda3\Library\bin
C:\Users\yourusername\anaconda3\Scripts
Now let’s create a shortcut to run Anaconda. In the window search bar at the bottom, search for “Anaconda Prompt” or “Anaconda Powershell Prompt” (either one is fine). Right click the icon in the Search Recent, select “Pin to start” or “Pin to taskbar.”
Click the pinned icon, a prompt window opens. It shows “(base) C:\Users\yourusername>.” (base) represents your current environment. The “base” is a default env.
You can run conda or pip commands to see what packages have been installed.
$conda list
$pip list
7. Create virtual environment for TyPorch
A virtual environment is an isolated environment for Python projects. Each project can have its own dependencies, regardless of what dependencies every other project has.
To run PyTorch, it is a good idea to create its own virtual environment. Open the Anaconda prompt window, and enter commands:
$conda create –name pytorch_env python=3.12
$conda activate pytorch_env
Now you are in the “pytorch_env” virtual env.
8. Install PyTorch
Go to PyTorch site again to copy the command at the bottom and run it in your Anaconda prompt.
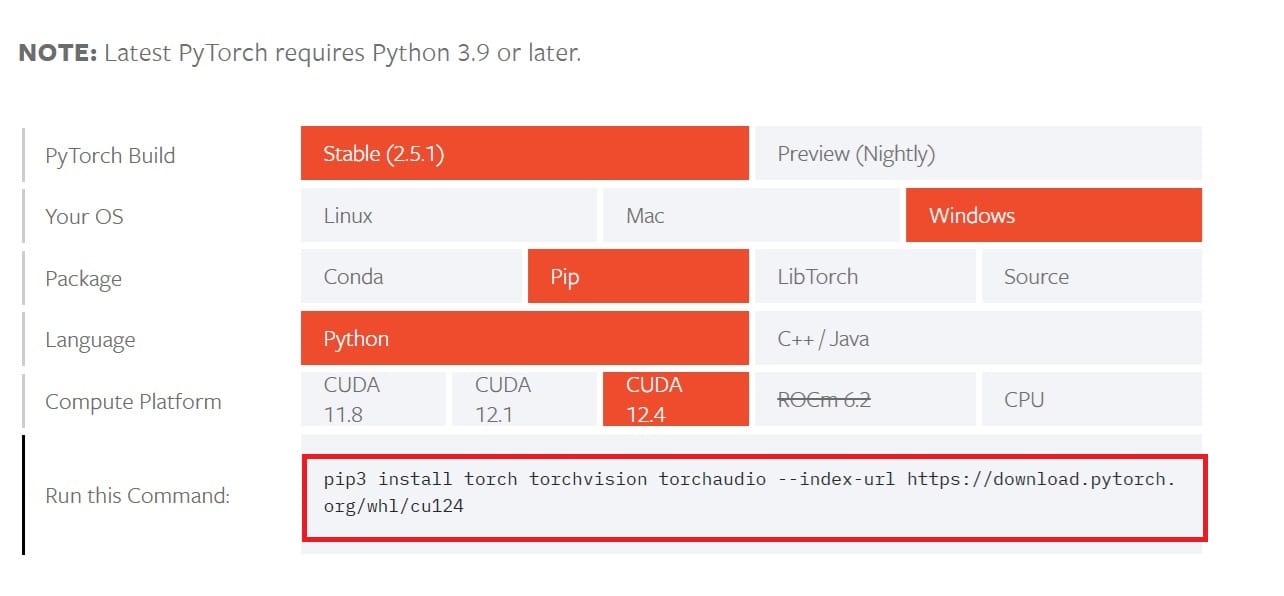
This command installs PyTorch and other commonly used packages such as NumPy.
$pip3 install torch torchvision torchaudio –index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu124
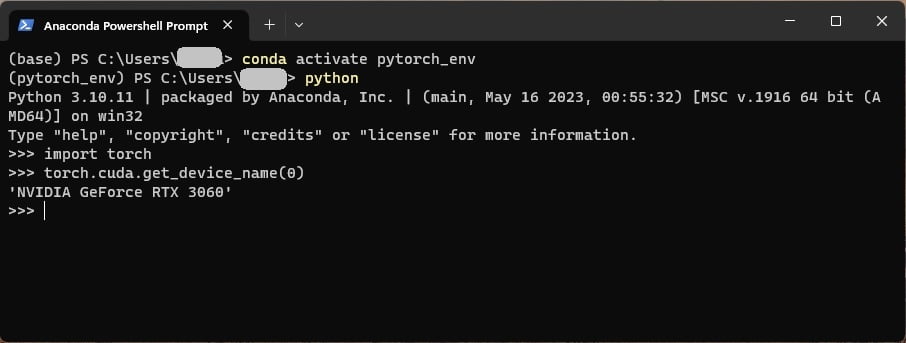
To check whether Pytorch is installed correctly with GPU support, run Python in the Anaconda prompt.
$python
Then run
>>>import torch
>>>torch.cuda.get.device_name(0)
If it returns your GPU card name, you have successfully installed PyTorch with GPU support.
9. Run your project
You can run Python code in the Anaconda prompt window. For example, enter commands:
$python app.py
Sometimes, you need to install additional packages or modules. You can run pip or conda in Anaconda prompt. For example,
$pip install ipython
$conda install -c conda-forge ffmpeg
Congratulations! Now you are ready to run PyTorch machine learning projects on your PC.
10. Install PyCharm
(This is optional.) PyCharm is an integrated development environment used for programming in Python. If you want to edit and run your project in PyCharm, you need to install it first. Go to Download PyCharm at jebrains site. Download the Community version and run the installer.
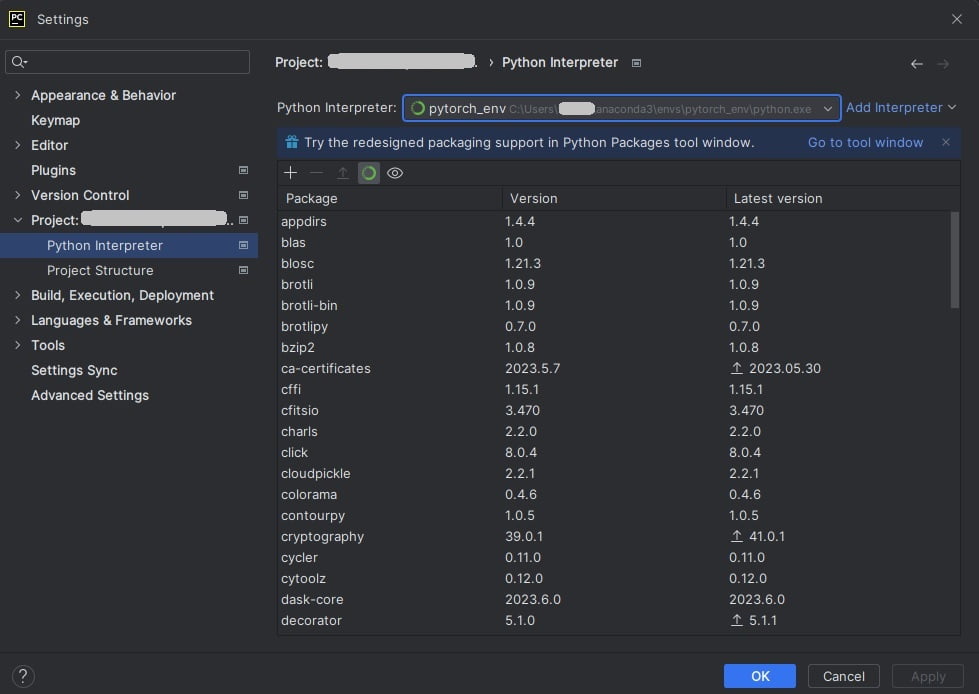
After installation, open PyCharm and create a new project. In the Python interpreter, check “Previously configured interpreter”. In the drop-down, select the “pytorch_env” you just created.
You can also change the interpreter for existing projects. Go to file->settings->project. In Python Interpreter, check “Using existing environment”, click “Add interpreter”, and select “pytorch_env”.